Introduction
This small guide is for players who are completely new to binary logic. It shows how the names of the gates correspond to words in a sentence and how they can be used to create circuits by simply describing what you see in a truth table.
This concept might be perceived as obvious for people with background knowledge, but is still something that each of us had to learn at some point.
Step 1: Describe The Green Outputs
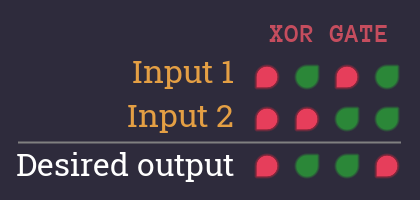










Let's take a look at the XOR level and its truth table
We want to describe each combination, that turns the desired output
What's the idea? If we make sure that our circuit outputs in all relevant cases, then it automatically outputs in all other cases. So we only have to focus on the and get the s for free.
Start like this:
There are 2 columns, that turn the desired output to .
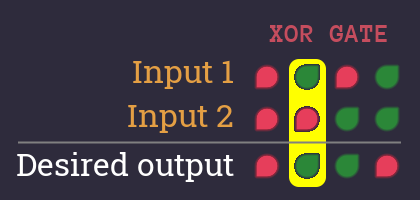
Let's start with the first and expand our descriptive sentence.
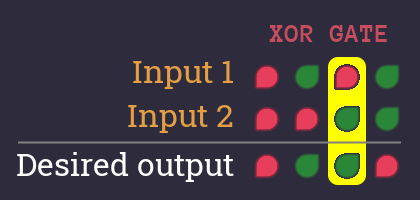
Nice! Okay that's the first column - now let's add the second.
We now have a complete description when our circuit outputs
Step 2: Replace 'Red' With 'Not Green'





We only focus on signals, that's why we try to avoid using the symbol in our description.
Here is the trick: When something is , we can also say it is 'not '.
So let's replace every symbol:
Step 3: Highlight The Gate Names

The connecting words in our sentence are also the name of gates!
Let's highlight all words, that are also names of gates and see what it looks like:
Notice, that i also added some brackets, since AND is a stronger connection than OR.
Step 4: Build The Circuit
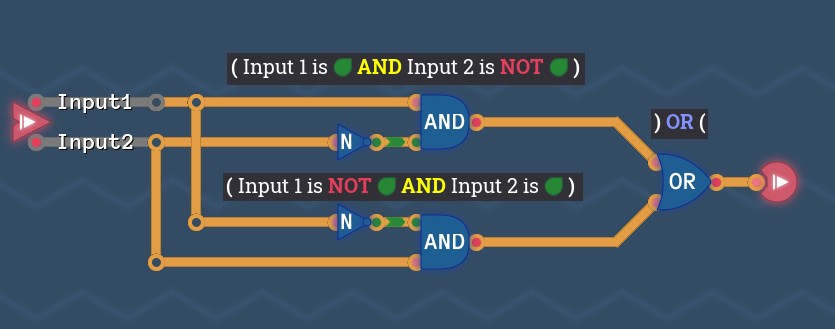
Now we can build a circuit that exactly matches our description, using the same gates that we highlighted in our sentence:
This technique works for every truth table.
The structure of resulting circuit is called Canonical Disjunctive Normal Form (CDNF) which can usually be optimized to require fewer gates (there are several techniques to achieve this).
Source: https://steamcommunity.com/sharedfiles/filedetails/?id=2949139905
More Turing Complete guilds
- All Guilds
- Turing Complete Guide 202
- Turing Complete: Basic Logic-Manual
- Robot Racing
- Turing Complete: Basic Logic-Solution
- Turing Complete: CPU Architecture-Solution
- Turing Complete: Arithmetic and Memory-Solution
- The 6502 Microprocessor
- Turing Complete: All-level walkthrough
- Turing Complete Guide 157
- / Turing Complete
